Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 20, №2, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Клінічний профіль та оцінка функції печінки в дітей, хворих на черевний тиф
Авторы: Ahmed Abdul Hadi Mohsen (1), Ghada Ali Yaqoob (2), Faris M. Al-Haris (3), Alaa Jumaah Manji Nasrawi (3)
(1) - College of Medicine, Jabir ibn Hayyan Medical University Najaf, Iraq
(2) - Al-Najaf Health Directorate, Iraq
(3) - University of Kufa, Faculty of Medicine, Iraq
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
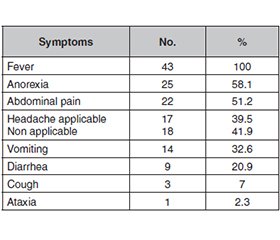
Актуальність. Черевний тиф все ще є серйозною проблемою охорони здоров’я в країнах, що розвиваються, із значною захворюваністю та смертністю. Він може призвести до пошкодження печінки, якщо його не лікувати належним чином. Ураження органа при черевному тифі проявляється в клінічних, біохімічних й гістопатологічних змінах. Метою цього дослідження є оцінка змін функції печінки на першому, другому та третьому тижнях у дітей, хворих на черевний тиф, а також клінічної картини й ускладнень протягом усього перебігу захворювання. Матеріали та методи. Це описове дослідження проведене з жовтня 2023 року по серпень 2024 року на базі лікарні Al-Zahraa Teaching Hospital for Maternity and Children в місті Al-Najaf (Ирак). Залучено 43 дитини (27 хлопчиків і 16 дівчаток) віком від 1 до 12 років із черевним тифом, діагностованим за клінічними ознаками та позитивним результатом серологічного тесту або посіву крові. Дослідження було розроблено таким чином, щоб включити клінічну інформацію, ускладнення та зміни функції печінки в кожного пацієнта. Результати. У дослідженні брали участь 19 дітей 1–5 років (44,2 %) і 24 (55,8 %) дитини віком від 6 до 12 років, хлопчиків було більше, ніж дівчаток (62,8 проти 37,2 %). В усіх пацієнтів виявлено лихоманку, у 25 (58,1 %) — анорексію, у 22 (51,2 %) — біль у животі, у 17 (39,5 %) — головний біль, у 14 (32,6 %) — блювання, інші симптоми спостерігалися рідше. Щодо ознак, то в більшості хворих була гепатомегалія — 19 (44,2 %), 12 (27,9 %) мали токсичний вигляд, болючість живота зареєстровано в 10 (23,3 %) випадках, спленомегалію — у 7 (16,3 %), набряки — у 2 (4,7 %), жовтяницю — у 2 (4,7 %), лише 1 (2,3 %) дитина мала висип на шкірі. Про гепатит повідомлено у 2 пацієнтів (4,7 %), перфорацію кишки — в інших 2 (4,7 %), в одного пацієнта був ендокардит (2,3 %), ще в одного — синдром Гієна — Барре (2,3 %). Параметрами функціональних тестів печінки, на які істотно впливав перебіг захворювання, були загальний білок сироватки крові (p < 0,001) і сироватковий альбумін (p < 0,001). Висновки. Черевний тиф частіше зустрічався у хлопчиків, ніж у дівчаток, і частіше в дітей віком 6–12 років. Він викликає різні ферментативні й біохімічні зміни, включаючи легке порушення ферментів печінки та значні зміни загального білка сироватки крові та сироваткового альбуміну, що можуть бути використані як лабораторні параметри для подальшого спостереження за пацієнтами з черевним тифом.
Background. Typhoid fever is still a major health problem in developing countries, with significant morbidity and mortality. The disease can lead to liver damage if not adequately treated. Liver involvement is known in typhoid fever in the form of clinical, biochemical, and histopathological changes. This study aims to assess the liver function changes on the first, second, and third weeks in children with typhoid fever and evaluate their clinical presentation and complications throughout the disease course. Materials and methods. This is a hospital-based descriptive study from October 2023 to August 2024 in Al-Zahraa Teaching Hospital for Maternity and Children in Al-Najaf City. We enrolled 43 children (27 male and 16 female) aged 1–12 years with typhoid fever diagnosed by clinical feature plus positive serology or blood culture. The study was designed to include clinical information, complications, and changes in liver function in each patient. Results. In this study, there were 19 children aged 1–5 years (44.2%) and 24 (55.8 %) cases between 6 and 12 years, males outnumbered females (62.8 vs 37.2 %). All patients presented with fever, 25 (58.1 %) with anorexia, 22 (51.2 %) with abdominal pain, 17 (39.5 %) with headache, 14 (32.6 %) with vomiting, and other symptoms were less frequent. Regarding signs, most patients had hepatomegaly — 19 (44.2 %), 12 (27.9 %) were toxic looking, abdominal tenderness was detected in 10 (23.3 %) children, splenomegaly in 7 (16.3 %), edema in 2 (4.7 %), jaundice in 2 (4.7 %), and only 1 (2.3 %) patient had skin rash. We reported hepatitis in 2 cases (4.7 %), intestinal perforation in other 2 (4.7 %), one patient had endocarditis (2.3 %) and another one Guillain-Barre syndrome (2.3 %). The parameters of liver function tests that were significantly affected through the disease course were total serum protein (p < 0.001) and serum albumin (p < 0.001). Conclusions. Typhoid fever was more common among males than females and more common in children aged 6–12. It causes various enzymatic and biochemical changes, including mild liver enzyme derangement and significant changes in total serum protein and serum albumin, which may be used as laboratory parameters for follow-up patients with typhoid fever.
черевний тиф; сальмонела; печінкові проби
typhoid fever; Salmonella; liver function tests
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Crump JA, Mintz ED. Global trends in typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(2):241-246.
- Mogasale V, et al. Burden of typhoid fever in low-income and middle-income countries: A systematic, literature-based update. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(10):e570-e580.
- Bhutta ZA. Current concepts in the diagnosis and treatment of typhoid fever. BMJ. 2006;333(7558):78-82.
- Khosla SN. Typhoid hepatitis. Postgrad Med J. 1990;66(776):471-473.
- Parry CM, et al. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(22):1770-1782.
- Agarwal S, et al. Hepatic dysfunction in typhoid fever. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(8):OC01-OC03.
- Sharma N, et al. Liver function tests in pediatric typhoid fever: A prospective study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;66(4):654-658.
- Devaranavadagi RA, Srinivasa S. A study on clinical profile of typhoid fever in children. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017;4(3):1067-1073.
- Ganesh R, Janakirama L, Vasanthi, et al. Profile of typhoid fever in children from a tertiary care hospital in Chennai-South India. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77(10):1089-1092.
- Saha A, Hassan MK, Kundu L, et al. Study of clinical profile and antibiotic response in typhoid fever at Faridpur Medical College Hospital. FMCJ. 2017;12:2-4.
- Gosai MM, Hariyani HB, Purohit PH, et al. A study of clinical profile of multidrug-resistant typhoid fever in children. NJIRM. 2011;2(3):87-90.
- Siddiqui SS, Shivraj Kumar Koppa, Kale AV. Clinical profile of typhoid fever in children at a tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017;4(6):1951-1954.
- Malini A, Barathy C, Madhusudan NS, Johnson C. Clinical and microbiological profile of enteric fever among pediatric patients in a tertiary care center in South India: A cross-sectional study. J Clin Sci. 2020;17(3):74.
- Alhares F, Albakaa A, Nasrawi A. Urinary tract infection in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Prensa Med Argent. 2020;106:6.
- Alshok MM. Typhoid fever complications in Babylon. Med J Babylon. 2004;1(2):149-154.
- Jagadish K, Patwari AK, Sarin SK, et al. Hepatic manifestations in typhoid fever. Indian Pediatr. 1994;31:807-807.
- Anusuya B, Sumathi S. Haematological alterations due to typhoid fever in Mayiladuthurai, Nagapattinam. Int J Res Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2015;2:210-216.
- Patankar N, Shah I. Age related clinical and laboratory manifestations of enteric fever in children. JK Science. 2009;11(3).
- Buzğan T, Evirgen Ö, Irmak H, et al. A case of typhoid fever presenting with multiple complications. Eur J Gen Med. 2007;4(2):83-86.
- Shamim A, Shamim A, Hussain B. Study of biochemical changes and elevated levels of enzymes in Salmonella typhi infected patients in Pakistani population. Int J Bioautomation. 2012;16(1):33-42.